Navigation
Denmark Announces Energy Consumption Down By 2.4% in Third Quarter 2011
Lower energy consumption for the first nine months of 2011 was reported on 16 February 2012 by the Danish Energy Agency.
 Middelgrunden offshore wind park. Danish wind turbines near Copenhagen.: Wind often flows briskly and smoothly over water since there are no obstructions. The large and slow turning turbines of this offshore wind farm near Copenhagen take advantage of the moderate yet constant breezes at this location. While the wind at this location is not strong it is very consistent, with the turbines generating substantial power over 97 percent of the time. Photograph courtesy of English Wikipedia, original upload 15 July 2004 by Leonard G.
Middelgrunden offshore wind park. Danish wind turbines near Copenhagen.: Wind often flows briskly and smoothly over water since there are no obstructions. The large and slow turning turbines of this offshore wind farm near Copenhagen take advantage of the moderate yet constant breezes at this location. While the wind at this location is not strong it is very consistent, with the turbines generating substantial power over 97 percent of the time. Photograph courtesy of English Wikipedia, original upload 15 July 2004 by Leonard G.
Lower energy consumption for the first nine months of 2011 was reported on 16 February 2012 by the Danish Energy Agency.
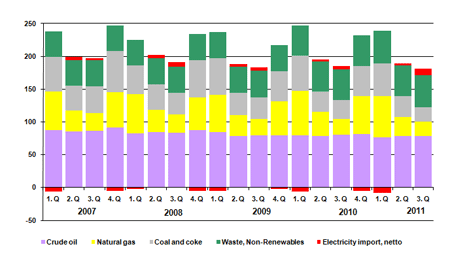
Observed energy consumption fell in the third quarter (Q3) 2011 by 2.4% compared to Q3 2010. Consumption of oil, natural gas and coal fell by 2.2%, 7.7% and 25.4% respectively. The large fall in consumption of coal can be explained by a fall in domestic electricity production for which coal is a dominant fuel. Consumption of renewable energy rose by 6.2% due to increased consumption of wind power and biofuels.
 Denmark Energy Consumption Down By 2.4% in Third Quarter 2011
Denmark Energy Consumption Down By 2.4% in Third Quarter 2011
The drop in electricity production was offset by an increase in net imports of electricity. Adjusted for fuel consumption linked to foreign trade in electricity, energy consumption went up by 0.7% in Q3.
Observed energy consumption for the first nine months of 2011 fell by 3.3% compared to the first nine months of 2010. Adjusted for fuels linked to net imports of electricity, energy consumption fell by 2.7%. The trend in energy consumption was affected by significantly warmer weather in 2011 than in 2010.
Primary energy production was 6.4% lower in Q3 2011 than in Q3 2010. Production of crude oil and natural gas fell by 4.6% and 14.5% respectively.
Primary energy production was 7.6% lower for the first nine months of 2011 than for the first nine months of 2010. This information is available at Monthly Energy Statistik 2011.
Securing Denmark’s Energy Future
The Danish Government’s plan "Our Future Energy" seeks to create green growth and help the country convert to 100 percent renewable energy use by 2050
The Danish Government presented on 25 November 2011 its plan for how the country can secure its energy future. Titled Our Future Energy, the strategy presents specific measures for fulfilling the Government’s goal of stimulating green growth. The plan is based on the previous government’s Energy Strategy 2050, but raises the bar higher.
The long-term goal of the plan is to implement an energy and transport network that relies solely on renewable energy sources. By 2020, the initiatives will lead to extensive reductions in energy consumption, making it possible for half of the country’s electricity consumption to be covered by wind power. Coal is to be phased out of Danish power plants by 2030. And by 2035, all electricity and heating will be generated using renewable sources.
The Minister for Climate, Energy and Building, Martin Lidegaard, says:
“Creating green economic growth will secure Denmark’s future. Viewed in narrow terms, we can expect to pay more for energy, but this has to be seen as a form of insurance. These are costly investments, but compared with the cost of what we’re insuring ourselves against, the amount is minimal. It’s a good investment if energy prices increase more than we forecast – and there is a significant risk of that happening."
“Investing in green energy can position Denmark in as a leader in developing climate-friendly technology. If Danish companies can capitalise on these opportunities, the country would benefit in the long run."
“The International Energy Agency warns that without a change in national energy policies, the global temperature will rise by six degrees by the end of this century. The initiatives in the government’s strategy will slash Denmark’s greenhouse gas emissions by 35 percent by 2020, compared with 1990 levels. That would put us well on the way towards meeting the EU’s goal of an 80 to 95 per cent reduction by 2050. If we can do this, it would send a signal to the world that establishing a green energy network is realistic and affordable in the long term."
Our Future Energy” calls for spending 5.6 billion kroner in 2020 on such initiatives as improved energy efficiency and expanding the use of renewable energy. Not included in that figure are the billions of kroner businesses and households are projected to invest in renewable energy and more efficient technologies. The decreased consumption that results from these investments will lead to lower overall energy costs. By 2020, the savings is projected to amount to 6.9 billion kroner, but would be even larger if the cost of fossil fuels increases.
The goal of a new energy policy should be to ensure the stability and security of our energy future, while simultaneously bringing Denmark closer to establishing a green energy network.
Notes:
Link to Our Future Energy (English translation)
Link to fact sheets (in Danish only)
Welcome to the Climate and Energy Guide This is an interactive guide with illustrations and links for further information.
See related article on the Horizon International Solutions Site
Search
Latest articles
Agriculture
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
Air Pollution
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Biodiversity
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
Desertification
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- UN Food Systems Summit Receives Over 1,200 Ideas to Help Meet Sustainable Development Goals
Endangered Species
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
- Coral Research in Palau offers a “Glimmer of Hope”
Energy
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
- Wildlife Preservation in Southeast Nova Scotia
Exhibits
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
- Coral Reefs
Forests
- NASA Satellites Reveal Major Shifts in Global Freshwater Updated June 2020
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Global Climate Change
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
Global Health
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- More than 400 schoolgirls, family and teachers rescued from Afghanistan by small coalition
Industry
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Natural Disaster Relief
- STOP ATTACKS ON HEALTH CARE IN UKRAINE
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
News and Special Reports
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- STOP ATTACKS ON HEALTH CARE IN UKRAINE
Oceans, Coral Reefs
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
Pollution
- Zakaria Ouedraogo of Burkina Faso Produces Film “Nzoue Fiyen: Water Not Drinkable”
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
Population
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
Public Health
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- STOP ATTACKS ON HEALTH CARE IN UKRAINE
Rivers
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
Sanitation
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Promoting the Development of Rural Water Supply and Sanitation -Case from Zhejiang Province, China
Toxic Chemicals
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Actions to Prevent Polluted Drinking Water in the United States
Transportation
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Urbanization Provides Opportunities for Transition to a Green Economy, Says New Report
Waste Management
- Promoting the Development of Rural Water Supply and Sanitation -Case from Zhejiang Province, China
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
Water
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- UN Food Systems Summit Receives Over 1,200 Ideas to Help Meet Sustainable Development Goals
Water and Sanitation
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems

